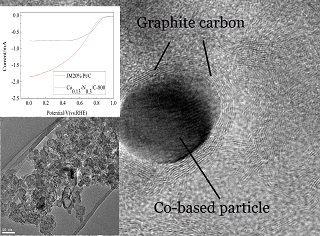
Transition metal-nitrogen co-doped carbon catalysts have attracted significant attention because of their reasonable activity and remarkable selectivity toward oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) as cathodic reaction in fuel cells. However, the role of transition metal in the active sites of the catalysts still is uncertain. In this work, the Cox-Ny/C-T catalysts were prepared with BP2000 as a carbon source, urea (Ur) as a nitrogen source and Co(OAc)2•4H2O as a metal precursor by a simple chemical method. Meanwhile, in order to optimize the ORR activity, the catalysts were synthesized with different amounts of Co and urea, and heat-treated at different temperatures from 600-1000 ℃. SEM, TEM, BET, XRD and XPS techniques were used to characterize the catalysts in terms of structures and compositions, as well as the catalytic active sites. CV and LSV were measured to compare the ORR activity and to obtain the electron transfer number. The peak potential for oxygen reduction was approximately 0.829 V (vs. RHE) on the optimum Co0.13-N0.3/C-800 catalyst in an alkaline electrolyte. The results indicated that Co-N-C was potentially catalytic active site and responsible for the ORR catalytic activity in an alkaline electrolyte. The overall electron transfer number for ORR catalyzed by the optimum Co-N/C catalyst was determined to be 3.7, suggesting that the ORR catalyzed by Co-N/C was a mixture of 2- and 4-electron transfer pathways, dominated by a 4-electron transfer process. Furthermore, the Cox-Ny/C-T catalysts also exhibited excellent methanol tolerance and stability.