

锂离子电池硅基负极材料的最新研究进展
收稿日期: 2016-05-11
修回日期: 2016-09-11
网络出版日期: 2016-09-12
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(No. 21321062,No. 21273185)、国家基础科学人才培养基金项目(No. J1310024)及福建省科技计划项目(No. 2013H6022)
Research Progress of Si-based Anode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries
Received date: 2016-05-11
Revised date: 2016-09-11
Online published: 2016-09-12
陈丁琼 , 杨阳 , 李秋丽 , 赵金保 . 锂离子电池硅基负极材料的最新研究进展[J]. 电化学, 2016 , 22(5) : 489 -498 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.160543
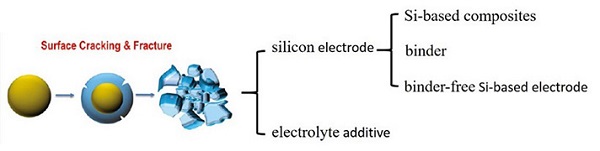
Owing to its high theoretical specific capacity (4200 mAh·g-1), silicon is a promising candidate to replace graphite as the anode in lithium ion batteries (LIBs). However, low intrinsic electric conductivity and dramatic volume change (~ 300%) during the process of lithiation and delithiation result in electrode pulverization and capacity loss with cycling, accordingly, the application of silicon as an anode in LIBs has been severely hindered. We will discuss the structure of silicon electrode including synthesis of Si-based composites,the selection of binder for silicon and the fabrication of binder-free Si-based electrode, as well as the electrolyte additive to improve the cycle performance of the battery.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |