

适用于钢筋混凝土腐蚀监测的长效MnO2参比电极的研制
收稿日期: 2016-03-28
修回日期: 2016-04-19
网络出版日期: 2016-05-18
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(No. 51371087)资助
Preparations of MnO2 Reference Electrodes for Corrosion Monitoring of Reinforced Concrete
Received date: 2016-03-28
Revised date: 2016-04-19
Online published: 2016-05-18
以电解法制备的MnO2粉体为原料,研制了可用于混凝土环境中的固体MnO2长效参比电极. 在饱和Ca(OH)2溶液中近一年的监测数据显示,该参比电极具有较好的电位稳定性和抗干扰能力,其电极电位的漂移< 10 mV. EIS和极化曲线测试结果表明,相对于化学法合成的MnO2电极,电解法制备的MnO2参比电极具有较小的内阻、较大的交换电流密度、较强的抗极化能力和较低的温度系数(~ 0.68 mV·°C-1). 在硬化砂浆中的长期测试表明,该电极在混凝土中的电极电位基本不受Cl-、有机胺阻锈剂的影响,能作为埋入式参比电极,满足混凝土中Cl-浓度、pH值和钢筋半电池电位的长期监测的要求,这对于海洋混凝土工程的耐久性监测具有较高的应用价值.
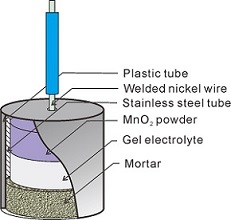
杨莉 , 徐兵 , 王海 , 董泽华 . 适用于钢筋混凝土腐蚀监测的长效MnO2参比电极的研制[J]. 电化学, 2017 , 23(1) : 36 -44 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.160328
In this work, the solid reference electrode was assemblied by using the electrochemically synthesized manganese dioxide (MnO2) (EMD) powder, gel electrolyte and thin mortar layer for the durability evaluation of concrete. The EMD reference electrode exhibited higher potential stability (< 10 mV drift) than the chemically synthesied MnO2 (CMD) based on half year potential tests in the saturated Ca(OH)2 solution and hardened mortar. In addition, the EMD electrode was almost insensitive to the presences of chloride ion and corrosion inhibitor. Electrochemical impedance and polarization curves indicate that the EMD electrode had lower charge transfer resistance,higher exchange current density and lower temperature coefficient than the CMD electrode. The EMD electrode could be a potential candidate as the long-term reference electrode for the durability management of concrete infrastructure.

[2] DU R G (杜荣归), Hu R G (胡融刚), Feng Z D (冯祖德), et al. Corrosion behavior of reinforcing steel in concrete[J]. Journal of Electrochemistry (电化学), 2000, 6(3): 305-310.
[4] Liu Y (刘玉), DU R G (杜荣归), Lin C J (林昌健). Effect of chloride ions on the corrosion behavior of reinforcing steel in simulated concrete pore solutions[J]. Journal of Electrochemistry (电化学), 2005, 11(3): 333-336.
[5] Wang J J (王静静), Dong S G (董士刚), Zhang X J (张小娟), et al. In situ detection on electrochemical chloride removal of reinforcement in concrete by combined pH/Cl- Probes[J]. Journal of Electrochemistry (电化学), 2014, 20(02): 95-100.
[6] Ansuini, J. F, Dimond J R. Factors Affecting the Accuracy of Reference Electrodes[J]. Materials performance. 1994, 33(11): 14-17.
[7] Elsener B. Corrosion rate of steel in concrete—Measurements beyond the Tafel law[J]. Corrosion Science. 2005, 47(12): 3019-3033.
[9] Zhang L L (张玲玲), Du M (杜敏), Yan M (颜民). Rsearch progress of refference electrode for engineering[J]. Corrosion Science and Protrction Technology (腐蚀科学与防护技术), 2006, 18(6): 433-435.
[10] Hu S X (胡士信). Development and performance evaluation of long life copper sulfate reference electrode[J]. Materials Protection (材料保护), 1991, 24(02): 24-27.
[12] Muralidharan S, Ha T, Bae J, et al. Electrochemical studies on the performance characteristics of solid metal–metal oxide reference sensor for concrete environments[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical. 2006, 113(1): 187-193.
[14] Muralidharan S, Saraswathy V, Madhavamayandi A, et al. Evaluation of embeddable potential sensor for corrosion monitoring in concrete structures[J]. Electrochimica Acta. 2008, 53(24): 7248-7254.
[15] Gao Y J (高永晶), Hao J L (郝敬丽), Dong Z H (董泽华). Preparation and properties of solid-state chloride ion selective electrode for detecting chloride ions in concrete[J]. Corrosion Science and Protrction Technology (腐蚀科学与防护技术), 2015, 27(03): 211-218.
[16] Montemor M F, Alves J H, Simões A M, et al. Multiprobe chloride sensor for in situ monitoring of reinforced concrete structures[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites. 2006, 28(3): 233-236.
[17] Xia X (夏熙) . The electrochemistry of manganese dioxide electrodes (1)[J]. Chinese Battery Industry (电池工业), 2005, 10(1): 54-56.
[18] Lu S (卢爽), Bang H J (巴恒静), Yang Y Z (杨英姿). MnO2 reference electrode for monitoring corrosion in concrete structures[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (武汉理工大学学报), 2009, 31(02): 42-45.
[19] Huang G S (黄国胜), Wu J H (吴建华), Chen G Z (陈光章). Fabrication and properties of manganese dioxide reference electrode[J]. Materials Protection (材料保护), 2005, 38(8): 39-41.
[20] Fan L (樊玲), Wei J (卫军), Peng S Q (彭述权), et al. Effect of alkaline electrolyte on performance of embedded MnO2 reference electrode[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (武汉理工大学学报), 2013, 35(12): 130-134.
[21] Fan L (樊玲), Wei J (卫军), Peng S Q (彭述权), et al. Studies on the performance characteristics of manganese oxide reference electrode for concrete environments[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors And Actuators (传感器学报). 2014, 27(06): 709-714.
[22] K N V, L B, A H. Production and characterisation of titanium doped electrolytic manganese dioxide for use in rechargeable alkaline zincrmanganese dioxide batteries[J]. Journal of power sources. 2000, 87(1): 205-211.
[23] X W, Y L. Synthesis and Formation Mechanism of Manganese Dioxide Nanowires/Nanorods[J]. Chemistry-a European Journal. 2003, 9(1): 300-306.
[24] Kuo P, Wu C, Lu C, et al. High Performance of Transferring Lithium Ion for Polyacrylonitrile-Interpenetrating Crosslinked Polyoxyethylene Network as Gel Polymer Electrolyte[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2014, 6(5): 3156-3162.
[25] Rakanta E, Zafeiropoulou T, G. B. Corrosion protection of steel with DMEA-based organic inhibitor[J]. Construction and Building Materials. 2013, 44: 507-513.
[26] Zhao B (赵冰), DU R G (杜荣归), Lin C J (林昌健). A study of three corrosion inhibitors for reinforcing steel in SPS solution by electrochemical methods[J]. Journal of Electrochemistry (电化学), 2005(04): 382-386.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |