

合成具有高氧还原反应催化活性的结构有序铂铁合金催化剂
收稿日期: 2015-12-30
修回日期: 2016-02-25
网络出版日期: 2016-04-28
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(21176022, 21376022,21476020),国际科技合作项目(2013DFA51860)资助
Synthesis of structurally ordered platinum-iron catalysts with enhanced oxygen reduction reaction activity
Received date: 2015-12-30
Revised date: 2016-02-25
Online published: 2016-04-28
为提高燃料电池用贵金属铂催化氧还原反应性能,采用改进的多元醇法制备不同金属比例的碳载铂铁合金催化剂(D-Pt3Fe/C和D-PtFe/C)前驱体. 随后通过优化在惰性气体环境中的高温煅烧条件,将结构无序的合金结构转变为结构有序的合金催化剂(O-Pt3Fe/C和O-PtFe/C). 利用X射线粉末衍射(XRD)、透射电子显微镜(TEM)、电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱(ICP-AES)和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)对所制得催化剂进行结构表征. 结果发现,所制得催化剂的合金纳米颗粒尺寸分布均一(4 ~ 6 nm),且均匀负载于碳载体上. 利用循环伏安法(CV)、线性扫描伏安法(LSV)对所制得催化剂进行电化学性能评估. 结果表明,O-PtFe/C的催化活性高于O-Pt3Fe/C,其质量活性(271.54 mA•g-1Pt)和比活性(0.73 mA•cm-2Pt)分别是商业JM Pt/C催化剂的4.3倍和7.3倍. 两种结构有序铂铁催化剂催化氧还原反应活性均高于商业JM Pt/C催化剂.
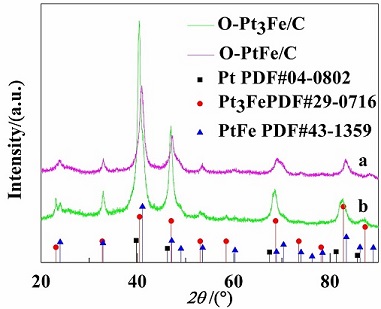
蔡业政 , 骆明川 , 王芳辉 , 孙照楠 , 朱红 . 合成具有高氧还原反应催化活性的结构有序铂铁合金催化剂[J]. 电化学, 2016 , 22(2) : 185 -191 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.151147
To improve oxygen reduction reaction catalytic activity of the precious metals platinum for fuel cell, the precursors of carbon-supported structurally disordered platinum-iron alloy (D-Pt3Fe/C and D-PtFe/C) catalysts with different compositions were synthesized via a modified polyol reduction method. Then, by optimizing the annealing conditions in the inert gas, we turned the structurally disordered platinum-iron alloy to the structurally ordered platinum-iron alloy (O-Pt3Fe/C and O-PtFe/C) catalysts. The structural characterizations of the as-prepared catalysts were performed by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The results showed that the as-prepared structurally ordered platinum-iron alloy nanoparticles with a small size in edge length of 4 ~ 6 nm were highly dispersed on the carbon support. The electrocatalytic performances of the as-prepared catalysts were evaluated by cyclic voltammetry (CV) and linear sweep voltammetry (LSV). It was found that the catalytic activity of O-PtFe/C was enhanced as compared to that of O-Pt3Fe/C. The mass activity and specific activity of O-PtFe/C are 271.54 mA•g-1Ptand 0.73 mA•cm-2Pt, respectively, which are 4.3 and 7.3 times higher than those of commercial JM Pt/C catalyst. The catalytic activities of both the as-prepared structurally ordered platinum-iron alloy catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction were higher than that of JM Pt/C catalyst.

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |