

银表面罗丹明6G的电化学表面增强拉曼光谱研究
收稿日期: 2015-08-19
修回日期: 2015-09-28
网络出版日期: 2015-11-09
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(No. 21227004,No. 21321062,No. J1310024,No. 21473140),科技部973项目(No. 2013CB933703,No. 2011YQ03012406)以及教育部创新团队基金(No. IRT13036)资助
Adsorption Behavior of Rhodamine 6G on Silver Surfaces Studied by Electrochemical Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
Received date: 2015-08-19
Revised date: 2015-09-28
Online published: 2015-11-09
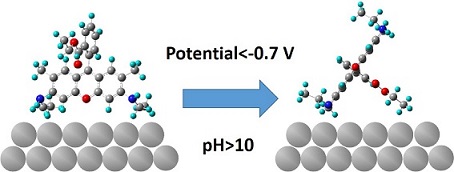
罗丹明6G(Rhodamine 6G,R6G)是单分子表面增强拉曼光谱(SM-SERS)研究中最常用的探针分子之一,对R6G分子在表面吸附行为的研究有助于了解R6G分子和表面的相互作用. 本文应用电化学和电化学表面增强拉曼光谱技术,研究不同电位下R6G的银电极表面的吸附行为. 结果表明,随着电位负移罗丹明6G在银表面上从垂直吸附转为倾斜吸附,该变化和碱性条件下吸附于金纳米粒子上R6G的吸附构象一致. 这说明,在部分单分子实验中所发现的R6G反常光谱其来源是单个R6G分子在表面吸附取向变化. 本研究对后续详细分析SM-SERS研究中单分子SERS谱峰变化的机制有一定的参考价值.
关键词: 罗丹明6G; 吸附取向; 电化学; 电化学表面增强拉曼光谱
陈婵娟 , 宗 铖 , 刘国坤 , 任 斌* . 银表面罗丹明6G的电化学表面增强拉曼光谱研究[J]. 电化学, 2016 , 22(1) : 32 -36 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.150819
Rhodamine 6G (R6G) is one of the most common probe molecules employed in single molecule surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SM-SERS). The study in adsorption behavior of R6G will help understand the interactions between R6G and surface. In this paper, we used electrochemical surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) to study the potential-dependent adsorption behavior of R6G on silver electrodes. Our results show that when the potential moved negatively, the orientation of R6G on silver surface changed from vertical to inclined adsorption. This result indicates that the abnormal SM-SERS spectra of R6G observed in the former SM-SERS studies from other research groups are due to the reorientation of the R6G molecule on the surface rather than the change in resonance effect of R6G. Such a detailed study will assist the understanding for the spectral change of SERS in SM-SERS studies.

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |