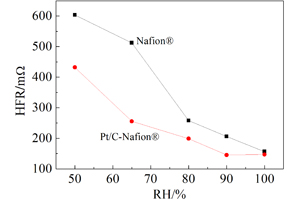
氢氧燃料电池的性能与质子交换膜的性能密切相关. 在燃料电池运行过程中,反应生成的水和加湿气体所含水的扩散渗透与膜内质子拖拽共同作用实现膜中水的平衡,影响膜的欧姆电阻,进而影响电池性能. 本文通过掺杂Pt/C对质子膜进行改性,并测试了改性膜的交流阻抗、吸水特性等物理性质和单电池性能及高频阻抗,说明由膜中的Pt/C催化剂原位催化渗透到膜中的氢气和氧气反应生成水,改善了电池低湿度运行时膜的含水率,从而降低膜电阻,提升电池性能.
The property of proton exchange membrane greatly affects the performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFC). During the operation of a PEMFC, the water produced at the cathode, the water vapor from the humidified feed gas and the water migrated by electro-dragging will reach a balance in the membrane and determine the resistance of PEMFC, and thus affect the performance of PEMFC. Normally, the PEMFC performance strongly depends on the relative humidity of the feed gas, and the performance decreases at lower humidity as a result of lower proton conductivity of the membrane. In this paper, we proposed to employ a Pt/C modified proton exchange membrane by promoting the H2 and O2 (that diffuse into the membrane from the feed gases) reactions in the membrane to produce water locally, and consequently improving the water content in the membrane. The AC resistance and water sorption property of the membrane, the performance and high frequency resistance of the cell prepared with home-made membrane were investigated in detail. It is found that the Ohmic resistance of the membrane was decreased under the same operation conditions and the PEMFC performance was greatly improved.
[1] Yi B L(衣宝廉). Fuel cells - principle, technology, application[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press(化学工业出版社), 2003: 1-8.
[2] Li X G. Principles of fuel cells[M]. CRC Press, 2006.
[3] Barbir F, Fomez T. Efficiency and economics of proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 1996, 21(10): 891-901.
[4] Zhang H W(张宏伟), Shen P K(沈培康). Research process of polymer electrolyte membrane for fuel cells[J]. Science China(中国科学:化学), 2012, 42(7): 954-982.
[5] Sahu A K, Pitchumani S, Shukla A K, et al. Nafion and modified-Nafion membranes for polymer electrolyte fuel cells: An overview[J]. Indian Academy of Sciences, 2009, 32(3): 285-294.
[6] Peihambardoust S J, Rowshanzamir S, Amjadi M. Review of the proton exchange membranes for fuel cell application[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(17): 9349-9384.
[7] Kundu S, Simon L C, Fowler M W. Comparison of two accelerated NafionTM degration experiments[J]. Polymer Degration and Stability, 2008, 93(1): 214-224.
[8] Springer T E, Zawadzinski T A, Gottesfeld S. Polymer electrolyte fuel cell model[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1991, 138(8): 2234-2342.
[9] Belkhiri Z, Zeroual M, Moussa H B, et al. Effect of temperature and water content on the performance of PEM fuel cell[J]. Revue des Energies Renouvelables, 2011, 14(1): 121-130.
[10] Amjadi M, Rowshanzamir S, Peihambardoust S J. Investigation of physical properties and cell performance of Nafion/TiO2 nanocomposite membranes for high temperature PEM fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(17): 9252-9260.
[11] Hiroyuki U, Yoshihiko U, Hiroki H, et al. Self-humidifying electrolyte membranes for fuel cells preparation of highly dispersed TiO2 particles in Nafion 112[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2003, 150(1): A57-A62.
[12] Choi W C, Kim J D, Woo S I. Modification of proton conducting membrane for reducing methanol crossover in a direct-methanol fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2001, 96: 411-414.
[13] Neburchilov V, Martin J, Wang H. A review of polymer electrolyte membranes for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 38: 169-221.
[14] Dimitrova P, Friedrich K A, Stimming U, et al. Modified NafionR-based membranes for use in direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Solid state ionic, 2002, 150(1/2): 115-122.
[15] Ma J X(马建新), Yi B L(衣宝廉), Yu H M(俞红梅), et al. Review on preparation method of membrane electrode assembly for PEMFC [J]. Progress in chemistry(化学进展), 2004, 16(5): 804-812.
[16] Sun K(孙琨). Preparation and characterization of novel proton exchange membrane based on Nafion[D], 2009.
[17] Watanabe M, Uchida H, Emori M. Analyses of self-humidification and suppression of gas crossover in Pt-dispersed polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cells[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1998, 14(4): 1137-1141.


