

PP14TFSI离子液体在可充镁电池电解液的应用
Application of Ionic Liquid PP14TFSI in Electrolyte Systems for Rechargeable Mg Batteries
Received date: 2013-07-16
Revised date: 2013-10-17
Online published: 2014-04-17
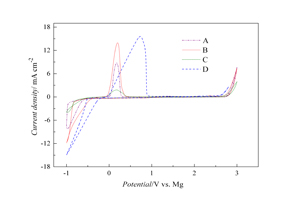
关键词: 苯酚基镁盐; N-甲基-N-丁基-哌啶-双三氟甲基磺酰胺; 可充镁电池; 混合溶剂; 电解液
朱金杰 , 王菲菲 , 郭永胜 , 杨军 , 努丽燕娜 , 王久林 . PP14TFSI离子液体在可充镁电池电解液的应用[J]. 电化学, 2014 , 20(2) : 128 -133 . DOI: 10.13208/j.electrochem.130726

/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |