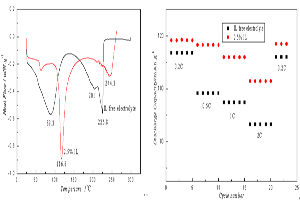
利用差示扫描量热仪(DSC)、电化学工作站、BTS电池测试系统、X-射线衍射仪(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和X射线能量色散谱(EDS)等方法,研究了含离子液体N-甲基丁基吡咯烷二(三氟甲基磺酰)亚胺盐(PyR14TFSI)电解液性能以及LiMn2O4电极高温电化学性能. 结果表明,随着1 mol·L-1 LiPF6 EC/EMC/DMC(1:1:1,by volume)中PyR14TFSI添加量的增大,电解液的电导率逐渐增大,添加量为2.5%(by mass)时,电解液DSC曲线由89.3 oC、201 oC、224 oC三个强吸热峰变为116.6 oC和244.3 oC两个强吸热峰;50 oC下,LiMn2O4倍率性能显著提高,2C放电比容量提高16 mAh·g-1,100循环周期后容量保持率为88.3%(提高2.2%). PyR14TFSI添加有利于电极结构的稳定.
In this work, with an aim to improve the performance of spinel lithium manganese and to reduce the safety concern of Li-ion battery system, the effects of N-methyl-N-butylpyrrolidinium bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide (PyR14TFSI) on performance of electrolyte and spinel lithium manganes are studied by using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), BTS battery test system, electrochemical work station, X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). The results indicate that the ionic conductivity of electrolyte is increased with the increase of PyR14TFSI concentration. When the concentration of PyR14TFSI is 2.5% (by mass), the DSC curves of the PyR14TFSI containing electrolyte are changed from three strong endothermic peaks (89.3 oC, 201 oC, 224 oC) to two strong endothermic peaks (116.6 oC, 244.3 oC). At 50 oC, the rate capability is enhanced, the discharge capacity is increased by 16 mAh·g-1, and the capacity retention is 88.3% (increased by 2.2%) after cycled for 100 times. PyR14TFSI is beneficial to the stability of the electrode structure.